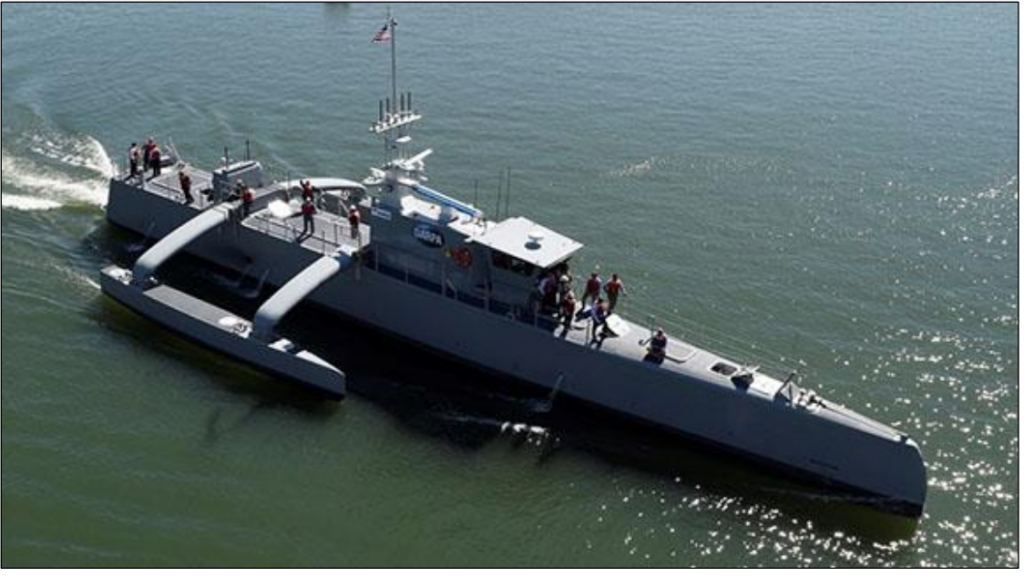
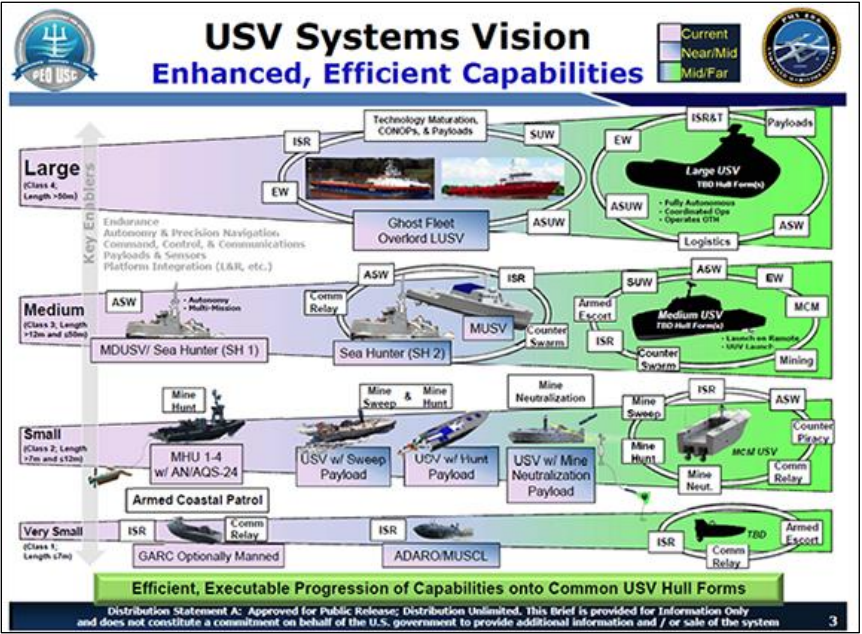
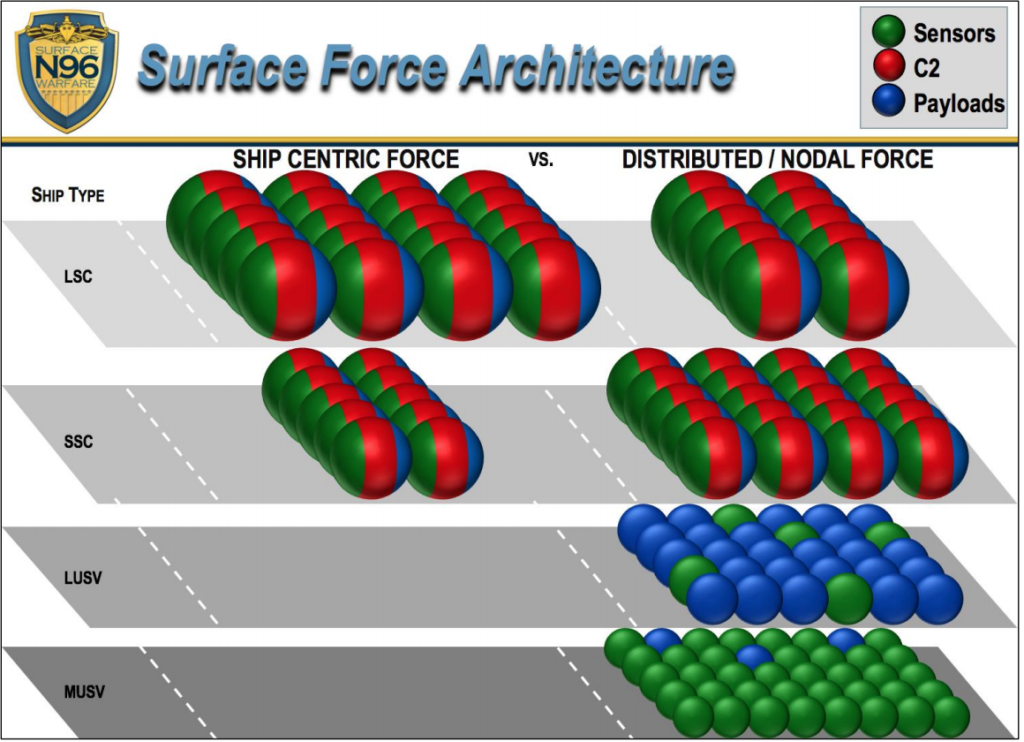
The world is constantly changing with the development of new technology. This is especially true with unmanned systems and supporting technology. There have been many successful implementations of unmanned systems in recent years for drones, self-driving cars, and automated vessels. This article is going to review the successful implementation of unmanned maritime vessels and the legal aspects of these systems.
SpaceX is known for its development of reusable rocket systems to reduce costs and make space travel more efficient for a future mission to deep space. These drone ships are autonomous and have many different capabilities that can be used remotely during the recovery of a rocket booster. The drone ships are not designed to move over long distances but are tugged to a location where they will adjust in short distances for the landing position of the rocket. The drone ships have firefighting capabilities, a robot to secure the rocket and a thruster to stabilize the ship (SpaceX Fleet, 2020).
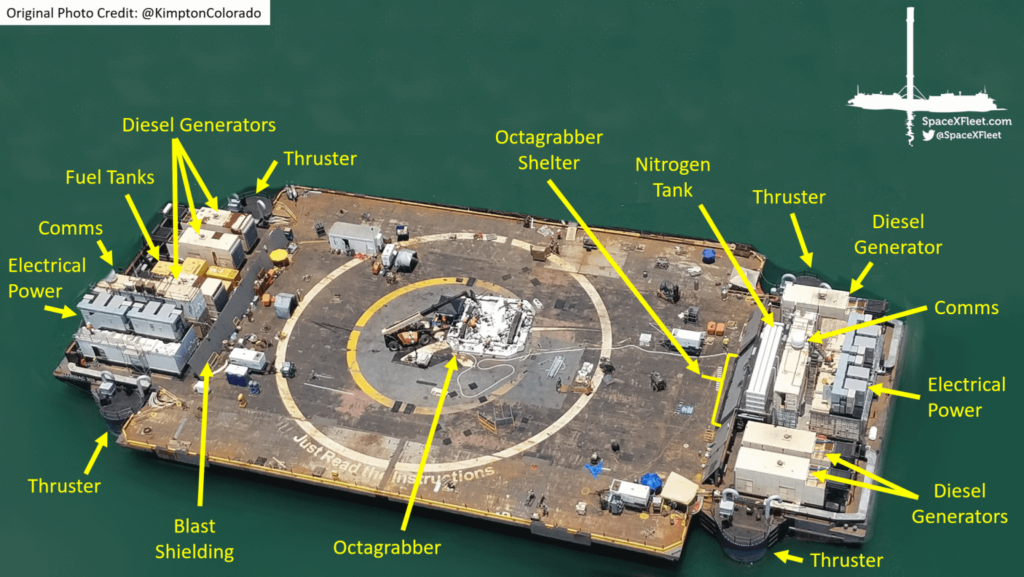
The SpaceX drone ship is only one successful implementation of an autonomous ship. There are many more for research and development and country defense. The only problems with unmanned vessels are the legalities of their operation and usage. Maritime laws that have been established have been focused on manned vessels and not the classification of unmanned systems (Norris, 2013). There are many debates on how to classify unmanned vessels. There are some thoughts that they should be classified as mines if they are tethered or immobile. Some thoughts are that there should be new classifications to cover all unmanned vessels (Delgado, 2018). Another topic of discussion is the navigational implications of their usage at sea. The navigational rights for ships clear for innocent, transit, and archipelagic sea lanes passage. However, these laws apply to manned ships (Delgado, 2018).
The classification of unmanned vessels is still up for debate and the need for classification is required before any other application to maritime laws can be applied. Classifying an unmanned vessel as a ship will apply the current maritime laws to the ship. The issue is the liability of the operator for the vessels. To date, there has not been a classification of unmanned vessels within the maritime laws (Norris, 2013). So, their responsibility and liability are lagging that of manned vessels. This is like the lagging of unmanned aerial vehicles for the Federal Aviation Administration.
The other topic of navigational rights is also in question. Maritime laws have three different rights of passage for vessels. These rights apply to manned ships, but it is unknown if unmanned ships can follow these same rights. The first right is the right of innocent passage. This right gives “ships of all states” the ability to navigate within the territorial sea of a coastal state (Norris, 2013). The second right is the right of transit passage. This allows ships and aircraft to transit through straights and overflight where the destination is another state. The last right is the archipelagic sea lane. The sea lanes are created by multiple states and all ships and aircraft can operate within these lanes (Norris, 2013).
By reviewing the navigation rights of maritime laws, it is easy to recognize the importance of classifying unmanned vessels or create a new classification to better fit the current laws that govern the seas. With the lack of classification, there is no clear answer to what unmanned vessels can do and their actions can be construed by each state. Unmanned maritime vessels will continue to be implemented for Navies, countries, and companies, so the need for these laws to be updated or applied are necessary for continued globalization.
References
Delgado, J. P. (2018). The Legal Challenges of Unmanned Ships in the Private Maritime Law: What Laws Would You Change? maritime, Port and Transport Law between Legacies of the Past and Modernization, 493-524.
Norris, A. (2013). Legal Issues Relating to Unmanned Maritime Systems Monograph. U.S. Naval War College.
SpaceX Fleet. (2020). Just Read the Instructions. Retrieved from SpaceX Fleet: https://spacexfleet.com/just-read-the-instructions